What are the advantages of precision parts processing and the expansion of the precision parts processing market?
by:Foxron
2021-11-10
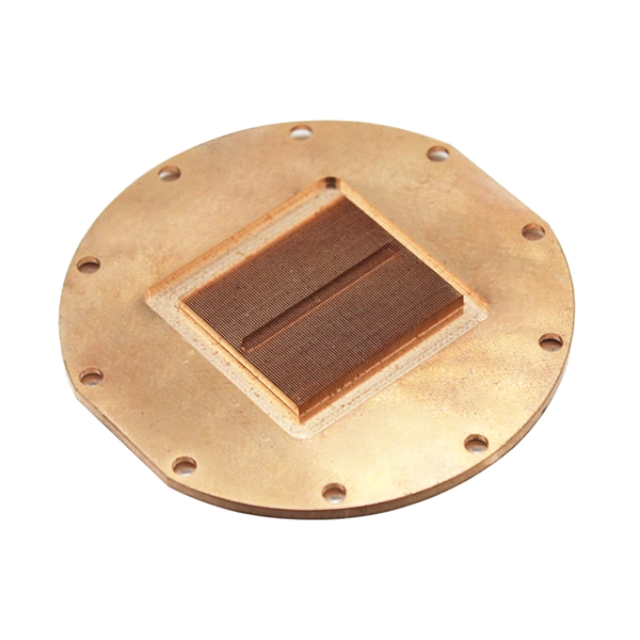
Precision forging forming technology refers to a part forming technology that can be used with little or no processing after the part is basically formed, also known as near-net forming technology. This technology is developed on the basis of conventional forging forming technology, and is an application technology that integrates computer information technology, new energy, and new materials. At this stage, precision forging forming technology is mainly used in precision forging parts and refined blanks.
Precision forging forming technology has obvious advantages, such as low cost, high efficiency, energy saving and environmental protection, and high precision. There are many types of this forming process, which are divided according to forming speed: high-speed precision forging, general precision forging, slow precision forging forming, etc.; based on metal flow conditions during the forging process: semi-closed, closed, and open precision forging forming processes ; Divided by forming temperature: superplastic, room temperature, medium temperature, high temperature precision forging forming, etc.; according to forming technology, divided into: split forging, isothermal forging, double dynamic forging, compound forming, warm precision forging, hot precision forging and cold precision Forging, etc. The division of precision forging technology according to forming technology has become a habitual classification method in production.
1. Compound forging
Multi-movement forging is also called occluded forging, this process is one of the more advanced precision forging technologies. This technology uses one punch to squeeze the inside of the closed groove one-way or two-way double-action squeeze to make the metal one-time forming. The formed part is a near-net precision forging without flash. The reason for using occluded forging is to increase the material usage rate and reduce the complexity of the processing process. The occlusive forging can form a complex profile and obtain a large amount of deformation in a single operation. It can save most of the cutting when producing complex parts and effectively reduce the cost.
2. Isothermal forging
Isothermal forging refers to the process of forging the blank material in a mold into a precision forging part at a constant temperature. Compared with conventional forging, isothermal forging can control the heating temperature of the blank within a certain range, so that the temperature during the forging process is approximately equal, and greatly improves the plastic change of the mold due to the sudden temperature change during the processing. Due to the technological characteristics of isothermal forging, it is especially suitable for precision forging of materials that are sensitive to deformation temperature or materials that are difficult to form, such as magnesium alloys and aluminum alloys.
3. Split forging
The important part of the split forging technology is to establish a material splitting channel in the forming part of the die or blank to ensure a good filling effect. When using this technology, in the process of filling the cavity with material, a part of the material is left in the shunt channel to form a shunt, which helps to fill the part that is difficult to form. The advantage of split forging is that this technology can avoid the closing device, has a good forming effect when forming gear parts, can achieve the required accuracy, does not require reprocessing after forming, and has a long mold life.
4. Isothermal forging
Isothermal forging refers to the process of forging the blank material in a mold into a precision forging part at a constant temperature. Compared with conventional forging, isothermal forging can control the heating temperature of the blank within a certain range, so that the temperature during the forging process is approximately equal, and greatly improves the plastic change of the mold due to the sudden temperature change during the processing. Due to the technological characteristics of isothermal forging, it is especially suitable for precision forging of materials that are sensitive to deformation temperature or materials that are difficult to form, such as magnesium alloys and aluminum alloys.
5. Cold precision forging forming
Forging metal materials without heating is called cold forging. There are mainly two technologies: cold heading and cold extrusion. Compared with other processes, its advantage is that the shape of the workpiece is easy to grasp, and there will be no deformation due to high temperature. The disadvantage is that the resistance during the deformation process is large and the plasticity of the workpiece is poor.
6. Compound precision forging forming
Compound precision forging forming process refers to the integration of technologies using multiple forging methods, or the combined use of other material forming technologies and forging processes. The processing materials and parts of the traditional technology have great limitations. The composite technology developed on the basis of the traditional technology can not only maximize the strengths and avoid the weaknesses, combine the strengths of each family, but also expand the scope of processing objects.
7. Hot precision forging forming
Hot precision forging forming technology is a kind of precision forging technology that seeks a suitable temperature as the processing temperature above the recrystallization temperature. However, compared with warm precision forging technology, due to the higher temperature selected, severe oxidation will occur, resulting in poor surface quality of forgings and insufficient precision of forgings.
8. Warm precision forging forming
Warm precision forging forming technology is a precision forging technology that finds a suitable temperature as the processing temperature below the recrystallization temperature. When choosing the temperature, it is better to choose the time when the plastic deformation of the metal is better, and before the strong oxidation occurs.
Precision forging forming technology has obvious advantages, such as low cost, high efficiency, energy saving and environmental protection, and high precision. There are many types of this forming process, which are divided according to forming speed: high-speed precision forging, general precision forging, slow precision forging forming, etc.; based on metal flow conditions during the forging process: semi-closed, closed, and open precision forging forming processes ; Divided by forming temperature: superplastic, room temperature, medium temperature, high temperature precision forging forming, etc.; according to forming technology, divided into: split forging, isothermal forging, double dynamic forging, compound forming, warm precision forging, hot precision forging and cold precision Forging, etc. The division of precision forging technology according to forming technology has become a habitual classification method in production.
1. Compound forging
Multi-movement forging is also called occluded forging, this process is one of the more advanced precision forging technologies. This technology uses one punch to squeeze the inside of the closed groove one-way or two-way double-action squeeze to make the metal one-time forming. The formed part is a near-net precision forging without flash. The reason for using occluded forging is to increase the material usage rate and reduce the complexity of the processing process. The occlusive forging can form a complex profile and obtain a large amount of deformation in a single operation. It can save most of the cutting when producing complex parts and effectively reduce the cost.
2. Isothermal forging
Isothermal forging refers to the process of forging the blank material in a mold into a precision forging part at a constant temperature. Compared with conventional forging, isothermal forging can control the heating temperature of the blank within a certain range, so that the temperature during the forging process is approximately equal, and greatly improves the plastic change of the mold due to the sudden temperature change during the processing. Due to the technological characteristics of isothermal forging, it is especially suitable for precision forging of materials that are sensitive to deformation temperature or materials that are difficult to form, such as magnesium alloys and aluminum alloys.
3. Split forging
The important part of the split forging technology is to establish a material splitting channel in the forming part of the die or blank to ensure a good filling effect. When using this technology, in the process of filling the cavity with material, a part of the material is left in the shunt channel to form a shunt, which helps to fill the part that is difficult to form. The advantage of split forging is that this technology can avoid the closing device, has a good forming effect when forming gear parts, can achieve the required accuracy, does not require reprocessing after forming, and has a long mold life.
4. Isothermal forging
Isothermal forging refers to the process of forging the blank material in a mold into a precision forging part at a constant temperature. Compared with conventional forging, isothermal forging can control the heating temperature of the blank within a certain range, so that the temperature during the forging process is approximately equal, and greatly improves the plastic change of the mold due to the sudden temperature change during the processing. Due to the technological characteristics of isothermal forging, it is especially suitable for precision forging of materials that are sensitive to deformation temperature or materials that are difficult to form, such as magnesium alloys and aluminum alloys.
5. Cold precision forging forming
Forging metal materials without heating is called cold forging. There are mainly two technologies: cold heading and cold extrusion. Compared with other processes, its advantage is that the shape of the workpiece is easy to grasp, and there will be no deformation due to high temperature. The disadvantage is that the resistance during the deformation process is large and the plasticity of the workpiece is poor.
6. Compound precision forging forming
Compound precision forging forming process refers to the integration of technologies using multiple forging methods, or the combined use of other material forming technologies and forging processes. The processing materials and parts of the traditional technology have great limitations. The composite technology developed on the basis of the traditional technology can not only maximize the strengths and avoid the weaknesses, combine the strengths of each family, but also expand the scope of processing objects.
7. Hot precision forging forming
Hot precision forging forming technology is a kind of precision forging technology that seeks a suitable temperature as the processing temperature above the recrystallization temperature. However, compared with warm precision forging technology, due to the higher temperature selected, severe oxidation will occur, resulting in poor surface quality of forgings and insufficient precision of forgings.
8. Warm precision forging forming
Warm precision forging forming technology is a precision forging technology that finds a suitable temperature as the processing temperature below the recrystallization temperature. When choosing the temperature, it is better to choose the time when the plastic deformation of the metal is better, and before the strong oxidation occurs.
Custom message










 Tel : 86 769 3325 6035 / 86 769 8306 2140
Tel : 86 769 3325 6035 / 86 769 8306 2140 Fax : +86 769 85634781
Fax : +86 769 85634781 E-mail :
E-mail :  Wechat//whatsapp : +86 189 3818 5885
Wechat//whatsapp : +86 189 3818 5885 Address : Wentang Industrial Zone, East District, Dongguan, Guangdong
Address : Wentang Industrial Zone, East District, Dongguan, Guangdong  Zip code : 523121
Zip code : 523121
