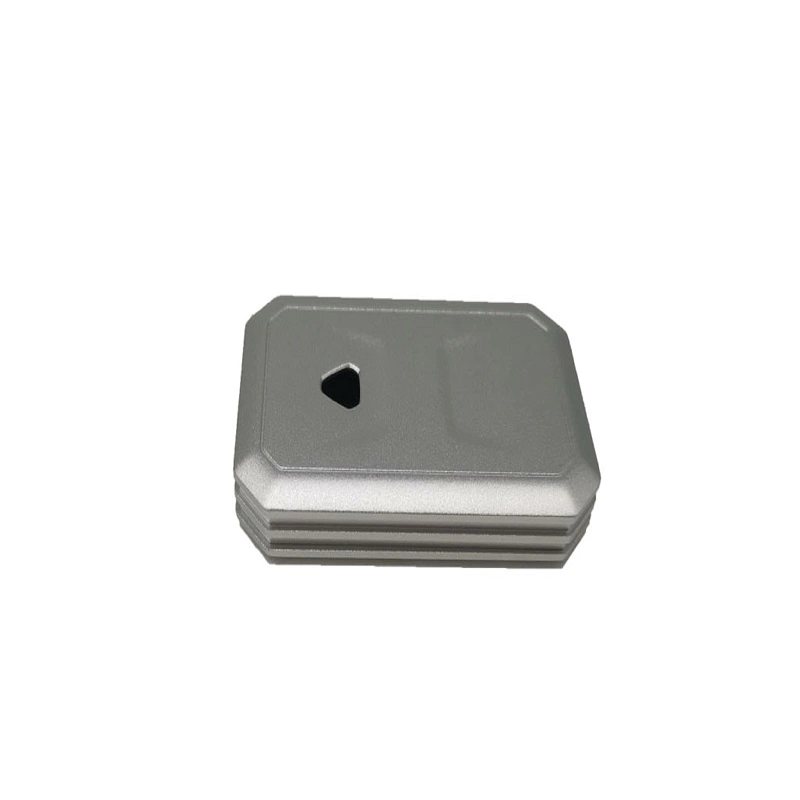
What are the aluminum alloy die castings for mold production?
by:Foxron
2021-11-16
Die-casting materials, die-casting machines, and molds are the three major elements of die-casting production, and none of them are indispensable. The so-called die-casting process is the organic and comprehensive application of these three elements to enable the stable, rhythmic and efficient production of qualified castings with good appearance, internal quality, and dimensions that meet the requirements of the drawing or agreement, or even high-quality castings. . The process of die-casting and filling the cavity is the process of obtaining the dynamic balance of pressure, speed, temperature and time. These processes are mutually restricted and interrelated. A balance must be achieved to obtain a perfect casting. My unit is mainly engaged in die casting of aluminum alloy, so this article mainly focuses on aluminum die casting molds, such as injection molds, stamping molds, etc. This article will not introduce the main components of die casting molds: fixed mold, fixed mold seat plate , Fixed mold set plate; movable mold, movable mold seat plate, movable mold set plate, support plate, core, insert, slider, sprue sleeve, shunt cone, exhaust plug, guide post, guide sleeve, push rod (Thimble) etc. Commonly used mold term: pouring system: the general term for the feed channel from the pressure chamber to the inner corner. Demolding slope (draft slope): The slope designed in the ejection or drawing direction of the mold wall for smooth release of the casting. Cavity: After the mold is closed, it is used to fill the molten alloy to form the cavity of the casting. Mold clamping force: The force applied to the mold in order to ensure that the dynamic and static molds are closely matched with each other during the filling process. Gate size and punch size: Gate size is determined by the shape of the casting. Because the injection speed and gate speed must meet certain numerical requirements during die casting, they must be fully considered in the mold design stage. Formula: Gate speed u003d(Cross-sectional area of u200bu200bpunch/cross-sectional area of u200bu200bgate)*Injection speed. General recommended conditions AL injection speed 1.5-2.5M/S gate speed thin wall 40-50M/S thick wall 35-45M/S. In the initial stage of redesign, it is recommended to use a plan that satisfies the conditions (injection speed 2M/S, gate speed 40M/S), and reserve conditions for expanding and adding gates after mold trial. Because the high-speed filling time is related to the molten metal flow of the casting, the solidification time calculation is also required: Tu003d0.01*(average wall thickness) Example: wall thickness 3mm solidification time tu003d0.01*3u003d0.09S(al) 2. Mold Temperature and mold accuracy The accuracy of the mold generally refers to the accuracy at room temperature. The occurrence of flash and mold sticking are all affected by the mold temperature of the casting conditions. If possible, design mold cooling holes as much as possible. When trying out the first set of molds, carefully check the heat distribution of the molds, and improve the design of better cooling holes for the second and third sets of molds. The principle of cooling distribution: the amount of cooling water away from the gate is small, and the amount of water close to the gate is large. When the slag bag is set up, the heat transfer from the product to the mold is controlled.
Custom message










 Tel : 86 769 3325 6035 / 86 769 8306 2140
Tel : 86 769 3325 6035 / 86 769 8306 2140 Fax : +86 769 85634781
Fax : +86 769 85634781 E-mail :
E-mail :  Wechat//whatsapp : +86 189 3818 5885
Wechat//whatsapp : +86 189 3818 5885 Address : Wentang Industrial Zone, East District, Dongguan, Guangdong
Address : Wentang Industrial Zone, East District, Dongguan, Guangdong  Zip code : 523121
Zip code : 523121
